New USGS report assesses successes, barriers, and lessons learned for decision-support tool design and development
Decision-support tools can be useful to natural resource managers, policy makers and other stakeholders that use USGS data. USGS scientists analyzed how scientists and technology professionals describe their experiences developing decision-support tools. In a new USGS report, they present five principles of successful decision-support tool design and development.
The USGS has provided trusted science to the public for decades, and decision-support tools are an important way that the Bureau gets targeted scientific information into the hands of those who need it for real-world decisions. Decision-support tools support diverse users and their decision needs. They can range from tools designed to analyze data for decision making to complex modeling applications. Decision-support tools help ensure that USGS science is actionable, but their effectiveness depends on the specifics of how tools are designed and developed.
A new USGS Scientific Investigations Report assesses successes, barriers, and lessons learned for decision-support tool design and development. The report aims to empower decision-support tool developers across USGS and beyond to create more robust, adaptable, and usable tools. Using information gathered from literature, web-based survey of USGS employees, and interviews with USGS employees, the report authors studied USGS experiences initiating, designing, and implementing decision-support tools including barriers to successful tool development. Of 54 survey respondents, 52% of respondents cited barriers being related to funding, 48% related to software, and 39% cited barriers related to stakeholder engagement. When asked “Are there any resources that you wish you had that would have helped during tool design and development?” the most mentioned responses were institutional support, funding, and staffing.
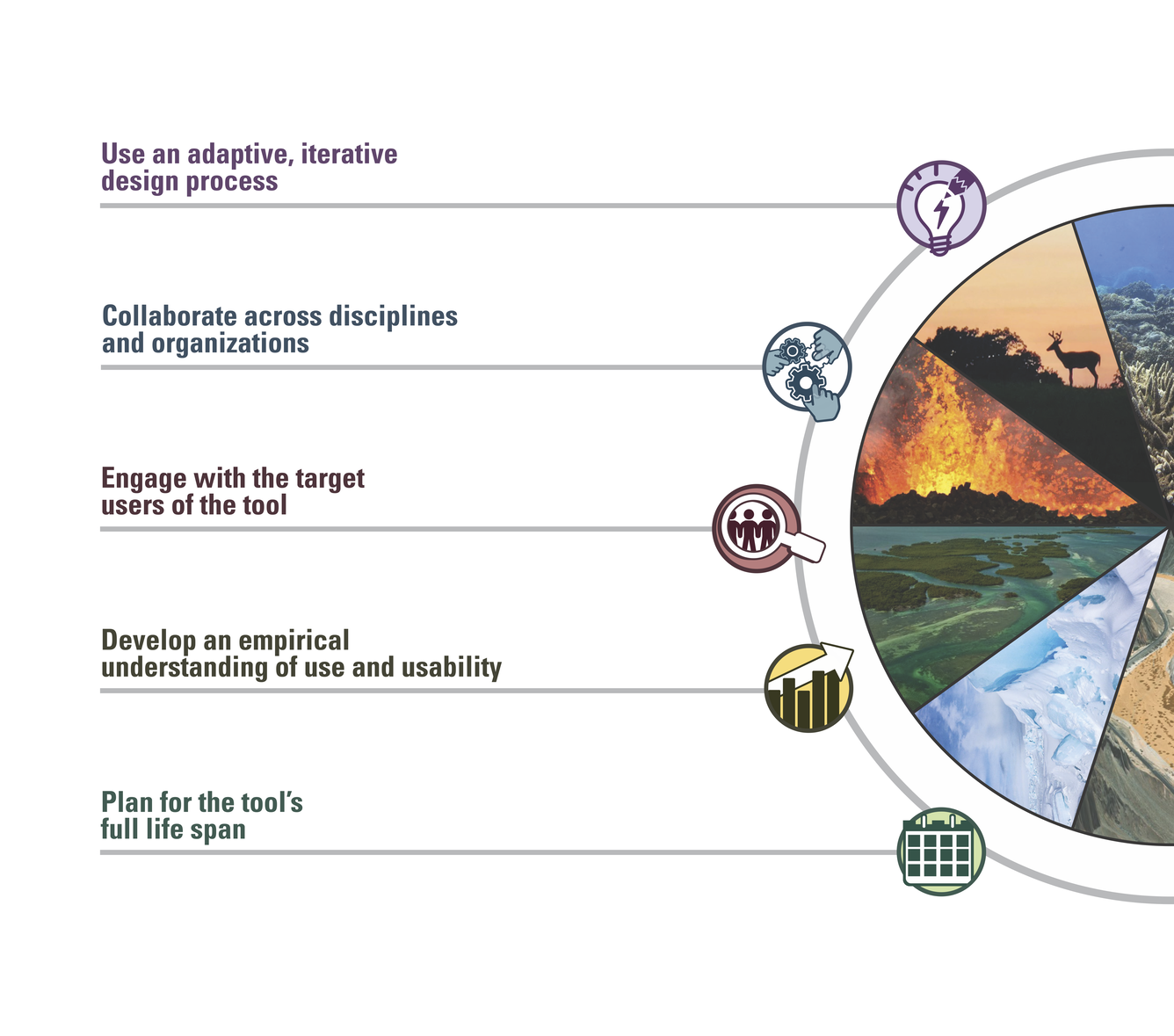
The report authors analyzed the information collected from the surveys, interviews, and the literature in order to identify best practices for decision-support tool design and development that apply both at USGS and more broadly. The authors present five guiding principles for tool development focused on human-centered design and user-centered design processes:
- Use an adaptive, iterative design process
- Collaborate across disciplines and organizations
- Engage with the target users of the tool
- Develop an empirical understanding of use and usability
- Plan for the tool’s lifespan
This report and the lessons learned from the experiences of employees across USGS improves the chances that every decision-support tool that the USGS chooses to invest in will be effective and used.
This research was a collaborative effort by staff from the USGS Ecosystems, Hazards, and Water Resources Mission Areas. The work was funded by the USGS Center for Data Integration.
Get Our News
These items are in the RSS feed format (Really Simple Syndication) based on categories such as topics, locations, and more. You can install and RSS reader browser extension, software, or use a third-party service to receive immediate news updates depending on the feed that you have added. If you click the feed links below, they may look strange because they are simply XML code. An RSS reader can easily read this code and push out a notification to you when something new is posted to our site.