CRSSP Imagery-Derived Requirements (CIDR) Tool Help Document
CRSSP Imagery-Derived Requirements (CIDR) Tool was designed to assist U.S. Federal Civil agencies to enter near-term land remote sensing data requirements. CIDR links to EarthExplorer (EE) allowing users to preview and download data for their requirement, and provides an interface to place new Data Acquisition Requests (DARS).
1. Registration and Login
CIDR utilizes the USGS EROS Registration System (ERS). Open the CIDR interface. Select the arrow icon on the top toolbar. Enter your ERS username and password then click the Sign In button to access all features of the CIDR tool. New users need to click on Create New Account to gain access to CIDR and EarthExplorer. The ERS Help Document has step-by-step instructions on the registration process.
Contact Customer Services at custserv@usgs.gov or (605) 594-6151 if you have any problems with the registration process. The Feedback link on the top toolbar can also be used to request assistance or to report errors.
2. New Data Acquisition Request (DAR)
The DAR provides an interface to initiate data acquisitions for new or existing events. The menu-based form facilitates the collection of remotely sensed data. Click Request Data on the toolbar just above the interactive map to open the menu.
A. Request Details
1. Project Description / Justification
Provide the name of your US Federal supported project and a brief description of the project, explaining why you need the data.
2. Data Use and Sharing
Describe who the data will be shared with.
The data may carry the restricted NextView License:
NextView License
- Image sharing must support a US Government purpose, with a direct benefit for US Government
- New imagery or imagery derived products must contain copyright and NextView license notice
- Sponsoring Federal Agencies must maintain US Government oversight of imagery distributed, end users, and downstream use
- US Federal Government employee or person authorized by a US Federal Government agency must authorize contractors, temporary users, and volunteers registering to use imagery
3. Output Format
Select GeoTiff, NTF, or No Preference from the dropdown menu for the desired output data format.
4. Has Scene List
If you have researched your area and know the scene IDs you need, select Yes. Someone will be contacting you to get the list of scenes.
B. Imaging Requirements
1. Username
This field will be autopopulated with your username.
2. Archived Imagery Needed
Select Yes or No from the dropdown menu. Yes indicates that you want currently archived data over your AOI. Select No if currently archived data is not wanted.
3. Publicly Viewable DAR
Select Yes or No from the dropdown menu. Yes indicates that you want the DAR viewable to other users. Select No if you require your DAR to be private.
4. Type of Imagery
Select Type of Imagery from the dropdown menu: Multispectral + Panchromatic, Multispectral, Panchromatic, Pansharpened, SAR/Radar, or Other. Only one type of imagery can be selected per DAR. An additional request will need to be submitted for each data type.
5. Image Resolution
Select Image Resolution from the dropdown menu. The Image Resolution options are determined by Type of Imagery and are populated after Type of Imagery has been entered.
6. Max Cloud Cover
Select the maximum cloud cover you will accept for your project’s data needs. Restricting the Max Cloud Cover to too small percentages may delay data acquisition if the cloud conditions are not met.
7. Acquisition Start
Enter the first acquisition date that you will accept for data for your project. If you are accepting archived imagery, put in the oldest date your will accept.
8. Acquisition End
Enter the last date you will accept collection of imagery, or the end date of archived imagery you will accept.
9. Repetitive Imaging Required?
This field allows for multiple data acquisitions. Select the frequency of requested data acquisition from the dropdown menu (No - Single Collection, Daily, Weekly, Bi-Weekly, or Monthly).
C. Request Details
Add any additional information you feel may be needed to get the data/product you need.
D. Spatial Requirements Section
Use the following controls to navigate the map:
Zoom - click the plus sign (+) to zoom in to the center of the map; click the minus sign (–) to zoom out. The mouse scroll wheel can also be used to zoom in or out.
Pan - click and drag the map to the desired location or view.
The Spatial Tools (Figure 1) allows users to define the area of interest by using the mouse or typing in the latitude and longitude. Coordinates can be displayed and entered as Decimal Degrees or Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds (DMS).
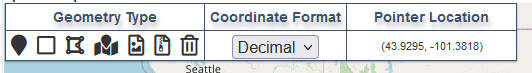
The Geometry Type tool allows users to define the area of interest by using the mouse or typing in the latitude and longitude.
Decimal degrees coordinates that are entered manually have a valid range of ± 90.00000 for latitude and ± 180.00000 for longitude (Figure 2). Negative values are used for south and west. A longitude of 99.0762 west would be entered as -99.0762.
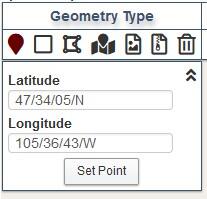
DMS coordinates that are entered manually need to be entered as Degree/Minute/Second/Direction with the direction indicated by N, S, E, or W (Figure 3).
Geometry Types include Point, Bounding Box, Multi-Point Polygon, Pre-defined Area (within the United States), KML Upload, or Shapefile Upload. The trash can icon can be used at any time to clear the map.
1. Point
To define a geographic location using a single point, select Point from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Click an area on the map once using the mouse to define a single point search.
The Latitude and Longitude can also be entered manually. Expand the Show Options window. Enter coordinates in decimal degrees then click on Set Point.
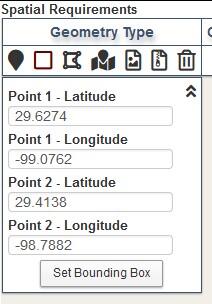
2. Bounding Box
To define a geographic location by creating a box, select Bounding Box from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Two points are used to define a bounding box - click on the map to indicate the upper left corner and the lower right corner for the area of interest (any opposite corners will work).
The latitude and longitude for the upper left corner and the lower right corner can also be entered manually. Expand the Show Options window. Enter coordinates for opposite corners of a box in decimal degrees then click on Set Point.
3. Multi-Point Polygon
To define a geographic location by creating a polygon, select Multi-Point Polygon from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Click multiple times on the map to define the area of interest. Up to 50 points can be used to create the polygon.
The Latitude and Longitude can also be entered manually. Expand the Show Options window. Enter coordinates in decimal degrees then click on Add Point. Add up to 50 points to complete the polygon.
4. Pre-defined Area
To define a geographic location using a pre-defined boundary (within the United States), select Pre-defined Area from the Geometry Type toolbar.
A menu of states, counties, and congressional districts are available for the United States. Select the desired location from the dropdown menus.
5. KML Upload
To define a geographic location using a KML file, select KML Upload from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Enter a Spatial Name for the area of interest. Use the Browse button to upload a Google Earth Keyhole Markup Language (KML) file. The KML file is limited to a single point or a multi-point single polygon. The uploaded KML file can be accessed through the Setting link on the top toolbar using the Spatial Name if additional data types are requested.
6. Shapefile Upload
To define a geographic location using a shapefile, select Shapefile Upload from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Enter a Spatial Name for the area of interest. Use the Browse button to upload the shapefile components. The shapefile dialog box requires .shp, .shx, .dbf, and .prj files for the upload. The shapefile is limited to a single point or a multi-point single polygon. The uploaded shapefile can be accessed through the Setting link on the top toolbar using the Spatial Name if additional data types are requested.
7. Clear Geometry
Click the garbage can icon to clear the geometry currently selected from any type of geometric selection.
E. Submit Request
Select the Submit button in the lower left hand corner of the screen. A status bar appears indicating that the request was successfully submitted and is awaiting approval (pending).
An automated email is sent to confirm the request and to provide a link to the DAR details. After leaving the CIDR site the request can be edited using the link in the email. DARs can only be edited while in pending status. The DAR can be shared with another emergency responder using the Email DAR Information link. Only one email address can be entered per transaction.
The DAR may be edited prior to approval. If additional Imagery Types are needed for the requirement, a copy of the DAR can be used as a template to create additional data requests.
The user will be able to track the status of the request and receive active notifications from the CIDR tool regarding any changes in the status of the request.
3. Data Collection
The CIDR Administrator reviews and approves pending requests, making basics modifications if necessary
4. Data Download or Order
Notification of new image availability is sent automatically to the requestor. When a new acquisition matches the search criteria, an email is sent to the requestor from the Standing Request module.
CRSSP Imagery-Derived Requirements (CIDR) Tool was designed to assist U.S. Federal Civil agencies to enter near-term land remote sensing data requirements. CIDR links to EarthExplorer (EE) allowing users to preview and download data for their requirement, and provides an interface to place new Data Acquisition Requests (DARS).
1. Registration and Login
CIDR utilizes the USGS EROS Registration System (ERS). Open the CIDR interface. Select the arrow icon on the top toolbar. Enter your ERS username and password then click the Sign In button to access all features of the CIDR tool. New users need to click on Create New Account to gain access to CIDR and EarthExplorer. The ERS Help Document has step-by-step instructions on the registration process.
Contact Customer Services at custserv@usgs.gov or (605) 594-6151 if you have any problems with the registration process. The Feedback link on the top toolbar can also be used to request assistance or to report errors.
2. New Data Acquisition Request (DAR)
The DAR provides an interface to initiate data acquisitions for new or existing events. The menu-based form facilitates the collection of remotely sensed data. Click Request Data on the toolbar just above the interactive map to open the menu.
A. Request Details
1. Project Description / Justification
Provide the name of your US Federal supported project and a brief description of the project, explaining why you need the data.
2. Data Use and Sharing
Describe who the data will be shared with.
The data may carry the restricted NextView License:
NextView License
- Image sharing must support a US Government purpose, with a direct benefit for US Government
- New imagery or imagery derived products must contain copyright and NextView license notice
- Sponsoring Federal Agencies must maintain US Government oversight of imagery distributed, end users, and downstream use
- US Federal Government employee or person authorized by a US Federal Government agency must authorize contractors, temporary users, and volunteers registering to use imagery
3. Output Format
Select GeoTiff, NTF, or No Preference from the dropdown menu for the desired output data format.
4. Has Scene List
If you have researched your area and know the scene IDs you need, select Yes. Someone will be contacting you to get the list of scenes.
B. Imaging Requirements
1. Username
This field will be autopopulated with your username.
2. Archived Imagery Needed
Select Yes or No from the dropdown menu. Yes indicates that you want currently archived data over your AOI. Select No if currently archived data is not wanted.
3. Publicly Viewable DAR
Select Yes or No from the dropdown menu. Yes indicates that you want the DAR viewable to other users. Select No if you require your DAR to be private.
4. Type of Imagery
Select Type of Imagery from the dropdown menu: Multispectral + Panchromatic, Multispectral, Panchromatic, Pansharpened, SAR/Radar, or Other. Only one type of imagery can be selected per DAR. An additional request will need to be submitted for each data type.
5. Image Resolution
Select Image Resolution from the dropdown menu. The Image Resolution options are determined by Type of Imagery and are populated after Type of Imagery has been entered.
6. Max Cloud Cover
Select the maximum cloud cover you will accept for your project’s data needs. Restricting the Max Cloud Cover to too small percentages may delay data acquisition if the cloud conditions are not met.
7. Acquisition Start
Enter the first acquisition date that you will accept for data for your project. If you are accepting archived imagery, put in the oldest date your will accept.
8. Acquisition End
Enter the last date you will accept collection of imagery, or the end date of archived imagery you will accept.
9. Repetitive Imaging Required?
This field allows for multiple data acquisitions. Select the frequency of requested data acquisition from the dropdown menu (No - Single Collection, Daily, Weekly, Bi-Weekly, or Monthly).
C. Request Details
Add any additional information you feel may be needed to get the data/product you need.
D. Spatial Requirements Section
Use the following controls to navigate the map:
Zoom - click the plus sign (+) to zoom in to the center of the map; click the minus sign (–) to zoom out. The mouse scroll wheel can also be used to zoom in or out.
Pan - click and drag the map to the desired location or view.
The Spatial Tools (Figure 1) allows users to define the area of interest by using the mouse or typing in the latitude and longitude. Coordinates can be displayed and entered as Decimal Degrees or Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds (DMS).

The Geometry Type tool allows users to define the area of interest by using the mouse or typing in the latitude and longitude.
Decimal degrees coordinates that are entered manually have a valid range of ± 90.00000 for latitude and ± 180.00000 for longitude (Figure 2). Negative values are used for south and west. A longitude of 99.0762 west would be entered as -99.0762.

DMS coordinates that are entered manually need to be entered as Degree/Minute/Second/Direction with the direction indicated by N, S, E, or W (Figure 3).

Geometry Types include Point, Bounding Box, Multi-Point Polygon, Pre-defined Area (within the United States), KML Upload, or Shapefile Upload. The trash can icon can be used at any time to clear the map.
1. Point
To define a geographic location using a single point, select Point from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Click an area on the map once using the mouse to define a single point search.
The Latitude and Longitude can also be entered manually. Expand the Show Options window. Enter coordinates in decimal degrees then click on Set Point.
2. Bounding Box
To define a geographic location by creating a box, select Bounding Box from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Two points are used to define a bounding box - click on the map to indicate the upper left corner and the lower right corner for the area of interest (any opposite corners will work).
The latitude and longitude for the upper left corner and the lower right corner can also be entered manually. Expand the Show Options window. Enter coordinates for opposite corners of a box in decimal degrees then click on Set Point.
3. Multi-Point Polygon
To define a geographic location by creating a polygon, select Multi-Point Polygon from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Click multiple times on the map to define the area of interest. Up to 50 points can be used to create the polygon.
The Latitude and Longitude can also be entered manually. Expand the Show Options window. Enter coordinates in decimal degrees then click on Add Point. Add up to 50 points to complete the polygon.
4. Pre-defined Area
To define a geographic location using a pre-defined boundary (within the United States), select Pre-defined Area from the Geometry Type toolbar.
A menu of states, counties, and congressional districts are available for the United States. Select the desired location from the dropdown menus.
5. KML Upload
To define a geographic location using a KML file, select KML Upload from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Enter a Spatial Name for the area of interest. Use the Browse button to upload a Google Earth Keyhole Markup Language (KML) file. The KML file is limited to a single point or a multi-point single polygon. The uploaded KML file can be accessed through the Setting link on the top toolbar using the Spatial Name if additional data types are requested.
6. Shapefile Upload
To define a geographic location using a shapefile, select Shapefile Upload from the Geometry Type toolbar.
Enter a Spatial Name for the area of interest. Use the Browse button to upload the shapefile components. The shapefile dialog box requires .shp, .shx, .dbf, and .prj files for the upload. The shapefile is limited to a single point or a multi-point single polygon. The uploaded shapefile can be accessed through the Setting link on the top toolbar using the Spatial Name if additional data types are requested.
7. Clear Geometry
Click the garbage can icon to clear the geometry currently selected from any type of geometric selection.
E. Submit Request
Select the Submit button in the lower left hand corner of the screen. A status bar appears indicating that the request was successfully submitted and is awaiting approval (pending).
An automated email is sent to confirm the request and to provide a link to the DAR details. After leaving the CIDR site the request can be edited using the link in the email. DARs can only be edited while in pending status. The DAR can be shared with another emergency responder using the Email DAR Information link. Only one email address can be entered per transaction.
The DAR may be edited prior to approval. If additional Imagery Types are needed for the requirement, a copy of the DAR can be used as a template to create additional data requests.
The user will be able to track the status of the request and receive active notifications from the CIDR tool regarding any changes in the status of the request.
3. Data Collection
The CIDR Administrator reviews and approves pending requests, making basics modifications if necessary
4. Data Download or Order
Notification of new image availability is sent automatically to the requestor. When a new acquisition matches the search criteria, an email is sent to the requestor from the Standing Request module.

