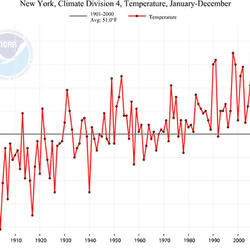
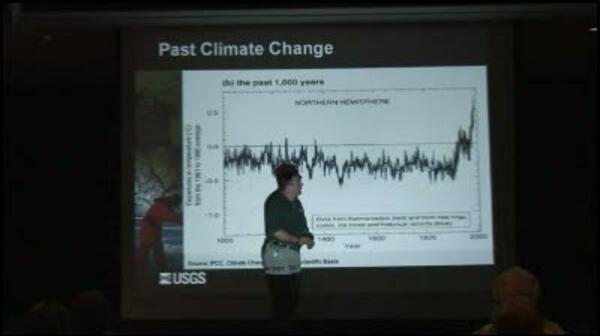
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from downtown Denver, Colorado. Questions include:
Why is climate change happening and what are the causes?
There are many “natural” and “anthropogenic” (human-induced) factors that contribute to climate change. Climate change has always happened on Earth, which is clearly seen in the geological record; it is the rapid rate and the magnitude of climate change occurring now that is of great concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat radiation. Human activity has increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere since the Industrial Revolution, leading to more heat retention and an increase in surface temperatures. Atmospheric aerosols alter climate by scattering and absorbing solar and infrared radiation and they may also change the microphysical and chemical properties of clouds. Finally, land-use changes, such as deforestation have led to changes in the amount of sunlight reflected from the ground back into space (the surface albedo).
Related
What are the long-term effects of climate change?
What is the difference between weather and climate change?
How can climate change affect natural disasters?
How do changes in climate and land use relate to one another?
How do we know the climate is changing?
What are some of the signs of climate change?
Does the USGS monitor global warming?
Will global warming produce more frequent and more intense wildfires?
Has the USGS made any Biologic Carbon Sequestration assessments?
How does carbon get into the atmosphere?
How much carbon dioxide can the United States store via geologic sequestration?
How much carbon dioxide does the United States and the World emit each year from energy sources?
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from downtown Denver, Colorado. Questions include:
 Climate Connections: Questions from Washington, DC
Climate Connections: Questions from Washington, DC
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from students at H.D. Woodson High School in Washington, DC. Questions include:
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from students at H.D. Woodson High School in Washington, DC. Questions include:
 Climate Connections: Questions from Glacier National Park, MT (Ep 4)
Climate Connections: Questions from Glacier National Park, MT (Ep 4)
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from the beautiful Glacier National Park in Montana. Questions include:
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from the beautiful Glacier National Park in Montana. Questions include:
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from Puerto Rico. Questions include:
- Why has the rainy season been so long in Puerto Rico?
- How is global warming impacting the island of Puerto Rico?
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from Puerto Rico. Questions include:
- Why has the rainy season been so long in Puerto Rico?
- How is global warming impacting the island of Puerto Rico?
 Climate Connections: Questions from North and South Carolina
Climate Connections: Questions from North and South Carolina
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from North and South Carolina.
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from North and South Carolina.
Climate change is an issue of increasing public concern because of its potential effects on land, water, and biological resources.
Climate change is an issue of increasing public concern because of its potential effects on land, water, and biological resources.
 USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
linkA new USGS program, the USA National Phenology Network, is recruiting tens of thousands of volunteers to team up with scientists to help track the effects of climate on seasonal patterns of plant and animal behavior.
USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
linkA new USGS program, the USA National Phenology Network, is recruiting tens of thousands of volunteers to team up with scientists to help track the effects of climate on seasonal patterns of plant and animal behavior.
A new method to assess the Nation's potential for storing carbon dioxide in rocks below the earth's surface could help lessen climate change impacts. The injection and storage of liquid carbon dioxide into subsurface rocks is known as geologic carbon sequestration.
An example of human activities that impact the earth's atmosphere.
An example of human activities that impact the earth's atmosphere.
Long-standing farming practices in California's Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta expose fragile peat soils to wind, rain and cultivation, emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and cause land subsidence. To capture or contain the carbon, farmers would ‘grow’ wetlands.
Characterizing urban heat islands across 50 major cities in the United States
Monitoring and assessing urban heat island variations and effects in the United States
Using information from global climate models to inform policymaking—The role of the U.S. Geological Survey
Changing Arctic Ecosystems: Updated forecast: Reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions required to improve polar bear outlook
Climate change: evaluating your local and regional water resources
Landsat Surface Reflectance Climate Data Records
U.S. Geological Survey Climate and Land Use Change Science Strategy—A Framework for Understanding and Responding to Global Change
Consequences of land use and land cover change
Changing Arctic ecosystems - measuring and forecasting the response of Alaska's terrestrial ecosystem to a warming climate
Polar bear and walrus response to the rapid decline in Arctic sea ice
The concept of geologic carbon sequestration
Assessing carbon stocks, carbon sequestration, and greenhouse-gas fluxes in ecosystems of the United States under present conditions and future scenarios
Related
What are the long-term effects of climate change?
What is the difference between weather and climate change?
How can climate change affect natural disasters?
How do changes in climate and land use relate to one another?
How do we know the climate is changing?
What are some of the signs of climate change?
Does the USGS monitor global warming?
Will global warming produce more frequent and more intense wildfires?
Has the USGS made any Biologic Carbon Sequestration assessments?
How does carbon get into the atmosphere?
How much carbon dioxide can the United States store via geologic sequestration?
How much carbon dioxide does the United States and the World emit each year from energy sources?
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from downtown Denver, Colorado. Questions include:
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from downtown Denver, Colorado. Questions include:
 Climate Connections: Questions from Washington, DC
Climate Connections: Questions from Washington, DC
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from students at H.D. Woodson High School in Washington, DC. Questions include:
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from students at H.D. Woodson High School in Washington, DC. Questions include:
 Climate Connections: Questions from Glacier National Park, MT (Ep 4)
Climate Connections: Questions from Glacier National Park, MT (Ep 4)
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from the beautiful Glacier National Park in Montana. Questions include:
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from the beautiful Glacier National Park in Montana. Questions include:
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from Puerto Rico. Questions include:
- Why has the rainy season been so long in Puerto Rico?
- How is global warming impacting the island of Puerto Rico?
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from Puerto Rico. Questions include:
- Why has the rainy season been so long in Puerto Rico?
- How is global warming impacting the island of Puerto Rico?
 Climate Connections: Questions from North and South Carolina
Climate Connections: Questions from North and South Carolina
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from North and South Carolina.
America has questions about climate change, and the USGS has real answers. In this episode of Climate Connections, USGS scientists answer questions gathered from North and South Carolina.
Climate change is an issue of increasing public concern because of its potential effects on land, water, and biological resources.
Climate change is an issue of increasing public concern because of its potential effects on land, water, and biological resources.
 USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
linkA new USGS program, the USA National Phenology Network, is recruiting tens of thousands of volunteers to team up with scientists to help track the effects of climate on seasonal patterns of plant and animal behavior.
USGS Public Lecture Series: Watching Nature's Clock: A Citizen-Scientist Effort to Track Seasonal Signs of Climate Change
linkA new USGS program, the USA National Phenology Network, is recruiting tens of thousands of volunteers to team up with scientists to help track the effects of climate on seasonal patterns of plant and animal behavior.
A new method to assess the Nation's potential for storing carbon dioxide in rocks below the earth's surface could help lessen climate change impacts. The injection and storage of liquid carbon dioxide into subsurface rocks is known as geologic carbon sequestration.
An example of human activities that impact the earth's atmosphere.
An example of human activities that impact the earth's atmosphere.
Long-standing farming practices in California's Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta expose fragile peat soils to wind, rain and cultivation, emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and cause land subsidence. To capture or contain the carbon, farmers would ‘grow’ wetlands.