This USGS streamgage on Schantz Spring near Wescosville, Pennsylvania was partially submerged after floodwaters from Tropical Storm Isaias quickly rose and flooded the area.
Multimedia
Images

This USGS streamgage on Schantz Spring near Wescosville, Pennsylvania was partially submerged after floodwaters from Tropical Storm Isaias quickly rose and flooded the area.

Fisseha Mengistu, USGS hydrologic technician, uses a device that lowers a water sampler into the creek below to collect samples used for water quality testing. Experts will be able to use this data to track how Tropical Storm Isaias impacted water quality in the area. This work was done on Rock Creek in Washington, D.C.
Fisseha Mengistu, USGS hydrologic technician, uses a device that lowers a water sampler into the creek below to collect samples used for water quality testing. Experts will be able to use this data to track how Tropical Storm Isaias impacted water quality in the area. This work was done on Rock Creek in Washington, D.C.
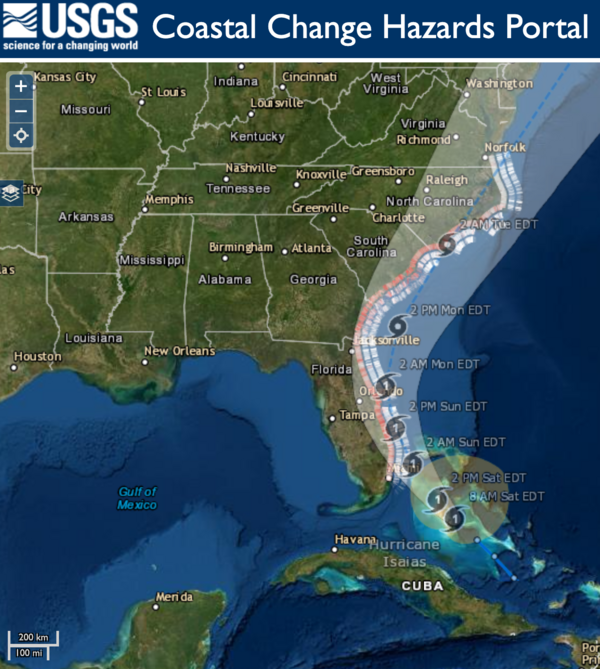
USGS coastal change experts predict that storm waves kicked up by the Category 1 hurricane are likely to cause some erosion at the base of the dunes along about 11 percent of coastal beaches between Florida and Virginia.
USGS coastal change experts predict that storm waves kicked up by the Category 1 hurricane are likely to cause some erosion at the base of the dunes along about 11 percent of coastal beaches between Florida and Virginia.

This USGS storm tide sensor was installed August 1 in North Myrtle Beach, South Carolina to measure the coastal impacts of Hurricane Isaias. Photo by Joshua Lee, USGS.
This USGS storm tide sensor was installed August 1 in North Myrtle Beach, South Carolina to measure the coastal impacts of Hurricane Isaias. Photo by Joshua Lee, USGS.

This rapid deployment gauge was installed August 1 in Swansboro, North Carolina on the White Oak River to monitor water levels in order track potential flooding caused by Tropical Storm Isaias. Photo by Bryce McClenney, USGS.
This rapid deployment gauge was installed August 1 in Swansboro, North Carolina on the White Oak River to monitor water levels in order track potential flooding caused by Tropical Storm Isaias. Photo by Bryce McClenney, USGS.
Videos
Before a hurricane, USGS Scientists undertake a data collection effort of a grand scale. They install a temporary mobile network of sensors along the coasts to collect additional data on the intensity of storm surge, one of the most dangerous elements of a hurricane.
Before a hurricane, USGS Scientists undertake a data collection effort of a grand scale. They install a temporary mobile network of sensors along the coasts to collect additional data on the intensity of storm surge, one of the most dangerous elements of a hurricane.


