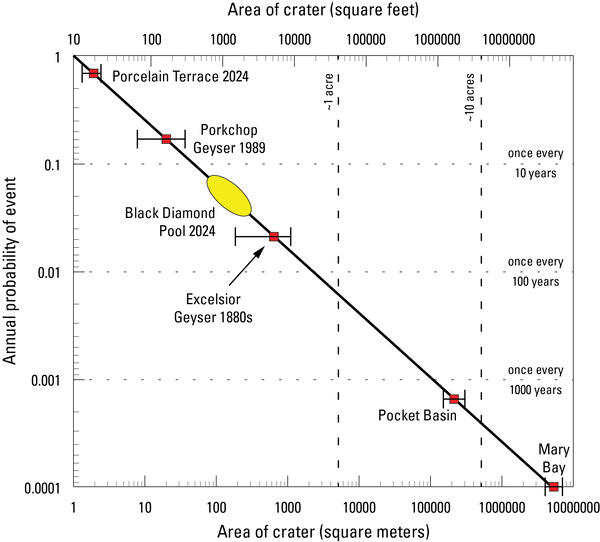
Plot of size versus annual probability for hydrothermal explosion craters in Yellowstone National Park
linkPlot of size versus annual probability for hydrothermal explosion craters in Yellowstone National Park. The line is a model based on the energy required to form a crater of a specific size, and it is fit to known hydrothermal explosion craters in Yellowstone National Park.