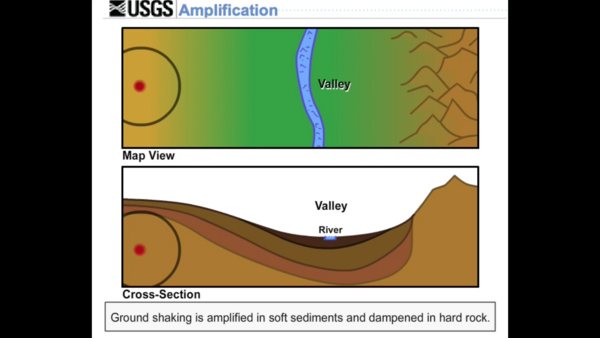
Shaking at a site may be increased, or amplified, by focusing of seismic energy caused by the materials in basins or by surface topography such as mountains.
Videos
Explore a wide variety of videos that highlight natural hazards, the risks they pose and the science we conduct to better understand and prepare for them.
Explore Earthquake Preparedness Videos
Earthquake hazards are a national risk, with nearly half of Americans living in areas prone to potentially damaging earthquakes. Learn about tools and resources that can help us all be better prepared.
Shaking at a site may be increased, or amplified, by focusing of seismic energy caused by the materials in basins or by surface topography such as mountains.
An asperity is an area on a fault that is stuck. The earthquake rupture usually begins at an asperity.
An asperity is an area on a fault that is stuck. The earthquake rupture usually begins at an asperity.
When you throw a pebble in a pond, it makes waves on the surface that move out from the place where the pebble entered the water. The waves are largest where they are formed and gradually get smaller as they move away. This decrease in size, or amplitude, of the waves is called attenuation.
When you throw a pebble in a pond, it makes waves on the surface that move out from the place where the pebble entered the water. The waves are largest where they are formed and gradually get smaller as they move away. This decrease in size, or amplitude, of the waves is called attenuation.
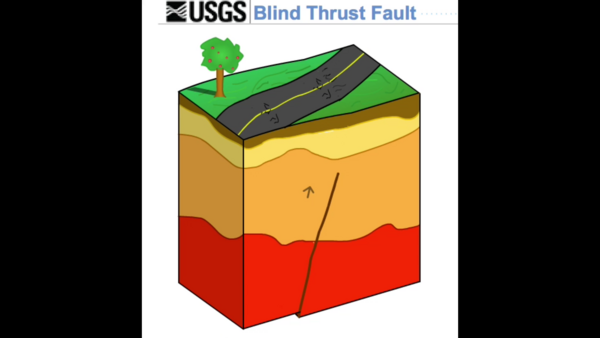
A thrust fault that does not rupture all the way up to the surface so there is no evidence of it on the ground. It is buried under the uppermost layers of rock in the crust.
A thrust fault that does not rupture all the way up to the surface so there is no evidence of it on the ground. It is buried under the uppermost layers of rock in the crust.
Directivity is an effect of a fault rupturing whereby earthquake ground motion in the direction of rupture propagation is more severe than that in other directions from the earthquake source.
Directivity is an effect of a fault rupturing whereby earthquake ground motion in the direction of rupture propagation is more severe than that in other directions from the earthquake source.
A divergent boundary is where two adjacent tectonic plates are moving away from each other.
A divergent boundary is where two adjacent tectonic plates are moving away from each other.
Elastic rebound is what happens to the crustal material on either side of a fault during an earthquake. The idea is that a fault is stuck until the strain accumulated in the rock on either side of the fault has overcome the friction making it stick.
Elastic rebound is what happens to the crustal material on either side of a fault during an earthquake. The idea is that a fault is stuck until the strain accumulated in the rock on either side of the fault has overcome the friction making it stick.
A horst is an upthrown block lying between two steep-angled fault blocks. A graben is a down-dropped block of the earth's crust resulting from extension, or pulling, of the crust.
A horst is an upthrown block lying between two steep-angled fault blocks. A graben is a down-dropped block of the earth's crust resulting from extension, or pulling, of the crust.
Liquefaction is a process by which water-saturated sediment temporarily loses strength and acts like a fluid... like when you wiggle your toes in the wet sand near the water at the beach. This effect can be caused by earthquake shaking.
Liquefaction is a process by which water-saturated sediment temporarily loses strength and acts like a fluid... like when you wiggle your toes in the wet sand near the water at the beach. This effect can be caused by earthquake shaking.
Normal, or Dip-slip, faults are inclined fractures where the blocks have mostly shifted vertically. If the rock mass above an inclined fault moves down, the fault is termed normal, whereas if the rock above the fault moves up, the fault is termed a Reverse fault.
Normal, or Dip-slip, faults are inclined fractures where the blocks have mostly shifted vertically. If the rock mass above an inclined fault moves down, the fault is termed normal, whereas if the rock above the fault moves up, the fault is termed a Reverse fault.
The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees that, for a given earthquake, that does not receive any direct P waves. The shadow zone results from S waves (not shown in animation) being stopped entirely by the liquid core and P waves being bent (refracted) by the liquid core.
The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees that, for a given earthquake, that does not receive any direct P waves. The shadow zone results from S waves (not shown in animation) being stopped entirely by the liquid core and P waves being bent (refracted) by the liquid core.
Strike-slip faults are vertical (or nearly vertical) fractures where the blocks have mostly moved horizontally. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the right, the slip style is termed right-lateral; if the block moves to the left, the motion is termed left-lateral.
Strike-slip faults are vertical (or nearly vertical) fractures where the blocks have mostly moved horizontally. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the right, the slip style is termed right-lateral; if the block moves to the left, the motion is termed left-lateral.
A thrust fault is a reverse fault with a dip of 45° or less, a very low angle. This animation shows a reverse fault which is a steeper-angle fault, but it moves the same way.
A thrust fault is a reverse fault with a dip of 45° or less, a very low angle. This animation shows a reverse fault which is a steeper-angle fault, but it moves the same way.
The wavefront is the instantaneous boundary between the seismic waves in the earth material, and the material that the seismic energy has not yet reached. As a seismic wave propagates through the earth, the wavefront moves.
The wavefront is the instantaneous boundary between the seismic waves in the earth material, and the material that the seismic energy has not yet reached. As a seismic wave propagates through the earth, the wavefront moves.
The shortest path between two points on the surface of a sphere lies along a great circle. On a 2-dimensional map, this looks like a line, but when it's on a 3-dimensional sphere, it's an arc... part of a circle.
The shortest path between two points on the surface of a sphere lies along a great circle. On a 2-dimensional map, this looks like a line, but when it's on a 3-dimensional sphere, it's an arc... part of a circle.
The USGS and its cooperators have installed debris-flow monitoring equipment in the largest drainage basin at Chalk Cliffs, CO. Data collection at this site supports research on the hydrologic factors that control debris-flow initiation, entrainment, and flow dynamics.
The USGS and its cooperators have installed debris-flow monitoring equipment in the largest drainage basin at Chalk Cliffs, CO. Data collection at this site supports research on the hydrologic factors that control debris-flow initiation, entrainment, and flow dynamics.
This time-lapse of Barter Island in Alaska during three summer months in 2014, shows the pack ice melting and the subsequent effects to the beach and permafrost cliffs from storms and summer temperatures. This camera sat on a fallen snow fence to capture storm events.
This time-lapse of Barter Island in Alaska during three summer months in 2014, shows the pack ice melting and the subsequent effects to the beach and permafrost cliffs from storms and summer temperatures. This camera sat on a fallen snow fence to capture storm events.
Changing sky conditions and smoke from the Slide fire, a major wildfire near Flagstaff, Arizona, are apparent in this sequence of natural-color, hemispheric images acquired on May 21, 2014. Individual images are collected at 10-minute intervals at the USGS Flagstaff Science Campus by the High Dynamic Range All-Sky Imaging System (HDR-ASIS).
Changing sky conditions and smoke from the Slide fire, a major wildfire near Flagstaff, Arizona, are apparent in this sequence of natural-color, hemispheric images acquired on May 21, 2014. Individual images are collected at 10-minute intervals at the USGS Flagstaff Science Campus by the High Dynamic Range All-Sky Imaging System (HDR-ASIS).
See English version already posted in Gallery
See English version already posted in Gallery
"1964 Quake: The Great Alaska Earthquake" is an eleven minute video highlighting the impacts and effects of America's largest recorded earthquake. It is an expanded version of the four minute video "Magnitude 9.2". Both were created as part of USGS activities acknowledging the fifty year anniversary of the quake on March 27, 2014.
"1964 Quake: The Great Alaska Earthquake" is an eleven minute video highlighting the impacts and effects of America's largest recorded earthquake. It is an expanded version of the four minute video "Magnitude 9.2". Both were created as part of USGS activities acknowledging the fifty year anniversary of the quake on March 27, 2014.
This Quicktime video shows a time-lapse sequence spanning from dawn to dusk on Tuesday, January 28, using images collected by our webcam near the summit of Mauna Loa Volcano (13,680 ft above sea level).
This Quicktime video shows a time-lapse sequence spanning from dawn to dusk on Tuesday, January 28, using images collected by our webcam near the summit of Mauna Loa Volcano (13,680 ft above sea level).