Data are collected every two minutes and sent by radio once per day to a server where values are plotted and released to the public internet.
Images
Images of Yellowstone.

Data are collected every two minutes and sent by radio once per day to a server where values are plotted and released to the public internet.

The Grey’s Landing Ignimbrite in Idaho (Dr. Thomas Knott, of the University of Leicester, England, gives the scale of the cliff). The entire cliff (and more not seen!) would have been deposited in a matter of moments as it welded to the land surface during a super eruption about 8.7 million years ago.
The Grey’s Landing Ignimbrite in Idaho (Dr. Thomas Knott, of the University of Leicester, England, gives the scale of the cliff). The entire cliff (and more not seen!) would have been deposited in a matter of moments as it welded to the land surface during a super eruption about 8.7 million years ago.

This two-image mosaic is one of the highest resolution views acquired by the Cassini spacecraft during its imaging survey of the geyser basin capping the southern hemisphere of Saturn's moon Enceladus.
This two-image mosaic is one of the highest resolution views acquired by the Cassini spacecraft during its imaging survey of the geyser basin capping the southern hemisphere of Saturn's moon Enceladus.

Photo of the Madison Museum, built in 1930 and designed by Herbert Maier. This structure exemplifies the National Park Rustic style, using natural materials and artisan craftmanship that are intended to blend buildings into the surrounding environment, “suggesting the smallness of man in relation to nature” (Herbert Maier).
Photo of the Madison Museum, built in 1930 and designed by Herbert Maier. This structure exemplifies the National Park Rustic style, using natural materials and artisan craftmanship that are intended to blend buildings into the surrounding environment, “suggesting the smallness of man in relation to nature” (Herbert Maier).
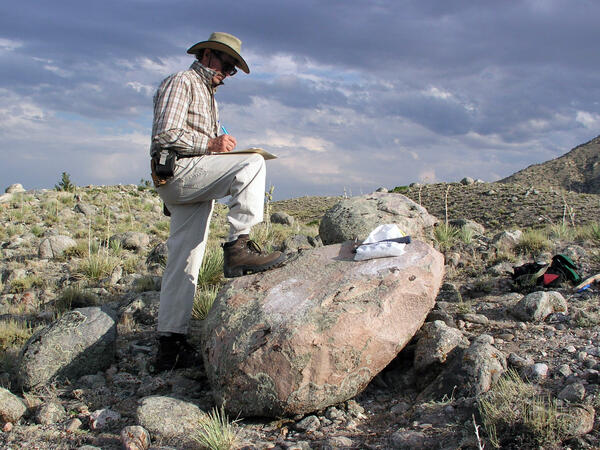

Ken Pierce in the field with a large glacial erratic in the Clarks Fork moraines taking detailed notes and annotating a map in progress.
Ken Pierce in the field with a large glacial erratic in the Clarks Fork moraines taking detailed notes and annotating a map in progress.

Bob Fournier measuring the gas-to-water ratio (gas/steam) at drill site Y2 in Yellowstone National Park
linkBob Fournier measuring the gas-to-water ratio (gas/steam) at drill site Y2, near Hot Lake on Firehole Lake Drive in Lower Geyser Basin, Yellowstone National Park, in the late 1960s. USGS Photo.
Bob Fournier measuring the gas-to-water ratio (gas/steam) at drill site Y2 in Yellowstone National Park
linkBob Fournier measuring the gas-to-water ratio (gas/steam) at drill site Y2, near Hot Lake on Firehole Lake Drive in Lower Geyser Basin, Yellowstone National Park, in the late 1960s. USGS Photo.

Hydrothermal explosion at Biscuit Basin in Yellowstone National Park. These types of events are the most likely explosive hazard from the Yellowstone Volcano.
Hydrothermal explosion at Biscuit Basin in Yellowstone National Park. These types of events are the most likely explosive hazard from the Yellowstone Volcano.
UNAVCO engineers drilling a borehole for instrument installation (left). Aerial view of borehole casing used to protect instruments from the elements found below the surface (right).
UNAVCO engineers drilling a borehole for instrument installation (left). Aerial view of borehole casing used to protect instruments from the elements found below the surface (right).

Gas flux measurement being taken over altered ground at Brimstone Basin, Yellowstone.
Gas flux measurement being taken over altered ground at Brimstone Basin, Yellowstone.

Gas flows up, appearing to boil, through the water of Alluvium Creek, Brimstone Basin, Yellowstone. Large funnel is used to trap gas, which is then sent to a collection bottle through the tubing.
Gas flows up, appearing to boil, through the water of Alluvium Creek, Brimstone Basin, Yellowstone. Large funnel is used to trap gas, which is then sent to a collection bottle through the tubing.

The water at Terrace Springs, northeast of Madison Junction in Yellowstone National Park, is relatively cold (about 60 °C or 140 °F), but the water is still saturated with CO2-rich bubbles. Photo by Shaul Hurwitz in September 2008.
The water at Terrace Springs, northeast of Madison Junction in Yellowstone National Park, is relatively cold (about 60 °C or 140 °F), but the water is still saturated with CO2-rich bubbles. Photo by Shaul Hurwitz in September 2008.

Narrow Gauge spring, Mammoth Hot Springs, Yellowstone National Park. Vent area is between the two trees on top of the travertine deposits. Terraced pools form due to deposition of travertine from the fluids as they cool and degas carbon dioxide.
Narrow Gauge spring, Mammoth Hot Springs, Yellowstone National Park. Vent area is between the two trees on top of the travertine deposits. Terraced pools form due to deposition of travertine from the fluids as they cool and degas carbon dioxide.
Left hand plot shows a focal mechanism from an earthquake where the fault is horizontal (red line), and the motion is right-lateral strike skip. The initial direction of wave motion (either back toward the source or away from the source is shown by the arrows. Right hand plot shows the associated beachball diagram, with compressional (“C”) and tensional
Left hand plot shows a focal mechanism from an earthquake where the fault is horizontal (red line), and the motion is right-lateral strike skip. The initial direction of wave motion (either back toward the source or away from the source is shown by the arrows. Right hand plot shows the associated beachball diagram, with compressional (“C”) and tensional
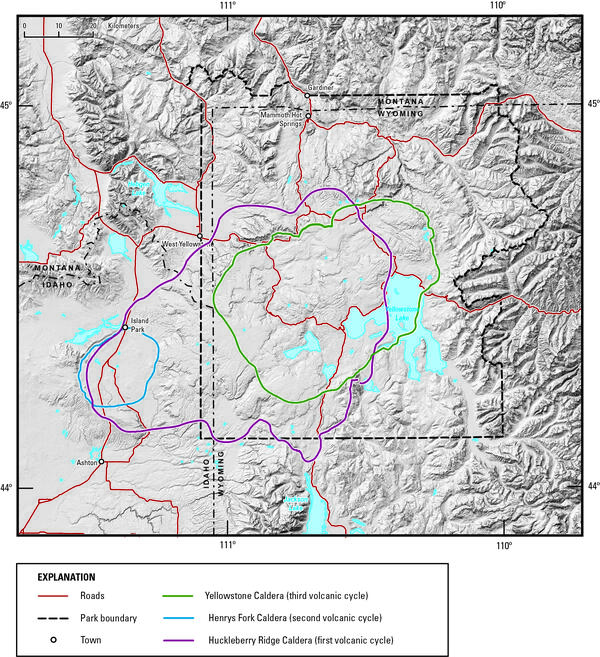
Digital elevation model of Yellowstone National Park and vicinity, showing the location of the calderas formed during each of Yellowstone’s three most recent volcanic cycles. The youngest caldera-forming eruption produced Yellowstone Caldera (green line), located within Yellowstone National Park.
Digital elevation model of Yellowstone National Park and vicinity, showing the location of the calderas formed during each of Yellowstone’s three most recent volcanic cycles. The youngest caldera-forming eruption produced Yellowstone Caldera (green line), located within Yellowstone National Park.

The contact (red arrow) between Huckleberry Ridge Tuff ignimbrite members B and C is marked by a time break of probably years to a few decades.
The contact (red arrow) between Huckleberry Ridge Tuff ignimbrite members B and C is marked by a time break of probably years to a few decades.

Southern tip of the Lemhi Range, eastern Snake River Plain. showing the wall of the Blue Creek caldera
linkSouthern tip of the Lemhi Range on the northeastern margin of the eastern Snake River Plain showing the caldera wall of the 6.27 million year old Blue Creek caldera, in the Heise volcanic field. Also shown are other units from the Heise volcanic field including the Kilgore Tuff and the Blacktail Creek Tuff. In the foreground is the much thicker sequence
Southern tip of the Lemhi Range, eastern Snake River Plain. showing the wall of the Blue Creek caldera
linkSouthern tip of the Lemhi Range on the northeastern margin of the eastern Snake River Plain showing the caldera wall of the 6.27 million year old Blue Creek caldera, in the Heise volcanic field. Also shown are other units from the Heise volcanic field including the Kilgore Tuff and the Blacktail Creek Tuff. In the foreground is the much thicker sequence

An eruption of Daisy Geyser in the Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park. The geyser erupts boiling water at about 93 °C (200 °F). Photo by Shaul Hurwitz on April 12, 2007.
An eruption of Daisy Geyser in the Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park. The geyser erupts boiling water at about 93 °C (200 °F). Photo by Shaul Hurwitz on April 12, 2007.

National Agriculture Imagery Program natural-color image from September 9, 2006, showing newly mapped thermal areas (outlined in yellow) on the north side of the Mallard Lake resurgent dome.
National Agriculture Imagery Program natural-color image from September 9, 2006, showing newly mapped thermal areas (outlined in yellow) on the north side of the Mallard Lake resurgent dome.

Guardian Geyser and Norris Geyser Basin, Yellowstone National Park.
Guardian Geyser and Norris Geyser Basin, Yellowstone National Park.

Aerial view of Excelsior Geyser (in the foreground) and Grand Prismatic Spring in Yellowstone’s Midway Geyser Basin. The colors around the thermal features are locations of different thermophile communities. These thermophiles fix carbon, both from the atmosphere and from the hot water. Credit Jim Peaco; June 22, 2006; Catalog #20386d; Original #IT8M4075
Aerial view of Excelsior Geyser (in the foreground) and Grand Prismatic Spring in Yellowstone’s Midway Geyser Basin. The colors around the thermal features are locations of different thermophile communities. These thermophiles fix carbon, both from the atmosphere and from the hot water. Credit Jim Peaco; June 22, 2006; Catalog #20386d; Original #IT8M4075
Old Faithful Geyser in eruption. Under Yellowstone Research Permit YELL-SCI-8030, 13 mineralized wood specimens were collected from the geyser mound. The dates of the mineralized wood samples imply that such eruptions did not take place for over a century between the mid-13th to mid-14th centuries.
Old Faithful Geyser in eruption. Under Yellowstone Research Permit YELL-SCI-8030, 13 mineralized wood specimens were collected from the geyser mound. The dates of the mineralized wood samples imply that such eruptions did not take place for over a century between the mid-13th to mid-14th centuries.




